No Results Found
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Ferroelectricity usually exists in a special class of dielectric materials. The spatial inversion symmetry of these materials is broken, so that the positive and negative charge centers of the system are separate, resulting in a spontaneous polarization. The direction of this spontaneous polarization can be reversed by the external electric field, resulting in a hysteresis loop1-2 similar to ferromagnetic materials, so this kind of property is called ferroelectric in analogy with ferromagnetism. In ferroelectric materials, the two electrical states of the electric polarization vectors before and after flipping can correspond to “0” and “1” in binary language respectively. Because the electrical state can be read and written repeatedly and preserved for a long time, ferroelectric materials are widely used in many fields, such as ferroelectric memory, ferroelectric tunnelling junction(FTJ)3, ferroelectric capacitor and ferroelectric diode. The traditional ferroelectric materials are mainly ABO3 type perovskite materials4.

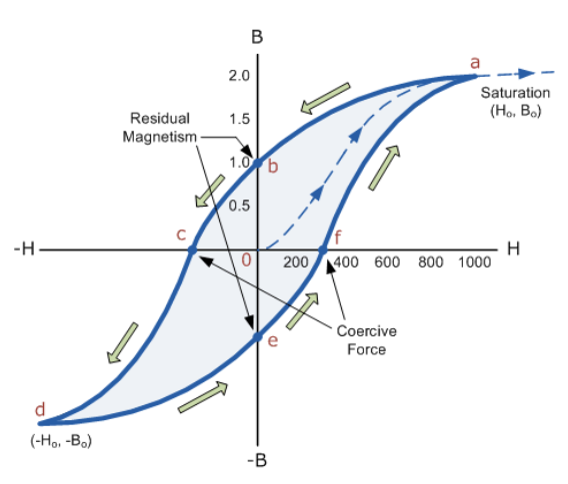
It shows the behaviour of a ferromagnetic core graphically as the relationship between B and H is non-linear. Starting with an unmagnetised core both B and H will be at zero, point 0 on the magnetisation curve1

(a) ABO3 cubic perovskite structure showing (b) the uniform strain in the crystalline cell with ferroelectric polarization and (c) flexoelectric induced polarization due to strain gradient4

Energy band diagrams of metal/ferroelectric (EE)/correlated electron oxide (CEO) FTJs for two polarization directions, in which the tunneling probability is controlled by the direction of the polarization, yielding either a hole accumulated (top) or a hole depleted (bottom) state in the CEO layer3
Under the general trend of miniaturization and integration of electronic equipment, exploring the new ferroelectric materials with small size and foldable properties has become a hot topic in the low dimensional ferroelectricity fields. In traditional ferroelectric materials (ABO3-type perovskite), when the thickness of the material reduce to several nanometers, the surface depolarization effect is strong, so that the ferroelectric property significantly weakened or even disappeared, corresponding to the ferroelectric critical size. Therefore, how to design and prepare high performance ferroelectric devices with small size has become one of the major challenges in this field.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Ji Group@Renmin University
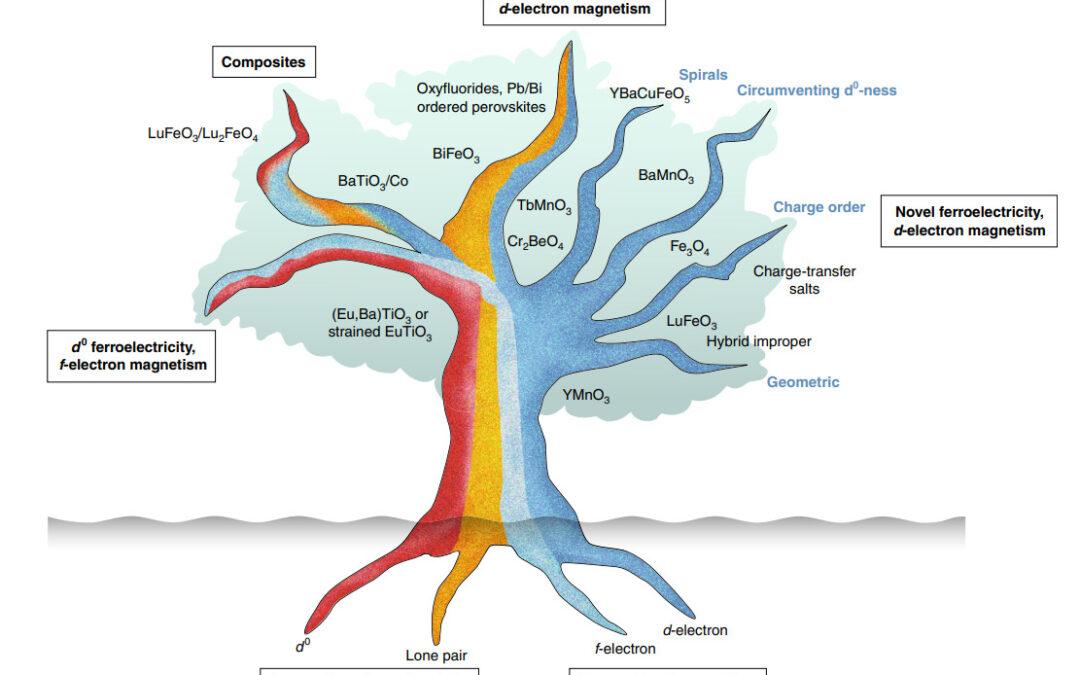

Fig.1 Multiferroic family tree[1]
Multiferroics exhibit more than one primary ferroic ordering, including ferromagnetism, ferroelectricity, or ferroelasticity in the same phase[1,2]. The terminology is usually extended to include non-primary orderings such as antiferromagnetism, antiferroelectricity, as well as composites of individual ferroics. The concept often used today is referred to magnetoelectric materiasl combing ferroelectric and magnetic behaviors (Fig. 1);. Such a combination of ferroic orders in multiferroics can lead to coupling between them and provide an efficient route to control magnetism by electric fields or vice versa.

Fig.2 Types of multiferroicity[3]
Multiferroics can be classified into two categories: type-I mulitferroics refer to the ferroelectricity does not have magnetic origin, which usually leads to an indirect and weak magnetoelectric coupling; Type-II multiferroics are induced by some specific magnetic orders with a strong magnetoelectric coupling but a small electric polarization and thus low transition temperature (TC). The two types are depicted in Fig. 2[3]
Ferroelectricity may be driven by electronic lone pairs, geometric effects, charge order or magnetism. In the first three classes, electric polarization and magnetism occur independently, i.e. the Type-I. In the last one, electric polarization and magnetic order emerge jointly, i.e. the Type-II.

Fig.3 Mechanisms in multiferroics[3]
The lone-pairs mechanism is based on spatial asymmetry caused by anisotropic distribution of unbonded valance electrons around the host ion (see Fig. 3a). In this case the material is a single-phase, containing two cations, with one provides the ferroelectricity and the other the magnetism. This mechanism originates from room-temperature ferroelectricity in BiFeO3. A pair of Bi3+ valance electrons in the 6s orbital in BiFeO3 is not involved in sp hybridization and creates a local dipole, which yields a spontaneous polarization[4] of ~100 μC/cm
In geometrically driven ferroelectrics, a small A-site cation permits rotations of its surrounding coordination polyhedral (Fig. 3b), which are either polar in their own right (for example, in BaNiF4[6]) or couple to a secondary polar distortion (as in YMnO3[7]). In this case, the polarization is both robust and small in magnitude. In h-RMnO3 (R=Sc, Y, In or Dy-Lu[8,9]), unit-cell tripling drives the emergence of a ferroelectric order at Tc ≥ 1,200 K with a polarization of 5.6 μC/cm2, followed by a magnetic ordering at the Neel temperature (TN ≤ 120 K).
Valance electrons can be distributed non-uniformly around their host ions in the crystal lattice to form a periodic superstructure (Fig. 3c). For example, the Fe atoms in LuFe2O4 may form a superlattice with an alternating sequence of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions[10]. This kind of charge ordering might be the source of an electric polarization.

In magnetically induced ferroelectrics, a non-collinear magnetic ordering, such as a spin spiral, breaks the inversion symmetry and induces a spontaneous polarization. These magnetically induced, so-called improper ferroelectric materials are totally different from displacive ferroelectrics, in which magnetic ordering is inhibited. The most intensely discussed mechanism is the inverse Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya (DM) interaction. Spin-orbit coupling (SOC) is crucial for the inverse DM interaction. The polarization is essentially determined by the optimization of the spin configuration from the point of view of anitsymmetry exchange, expressed by the antisymmetric product Si × Sj of neighboring spins Si,j (see Fig. 3d). The polarization vector is P ∝ eij × ( Si × Sj), where eij is the unit vector connecting neighboring spins. Multiferroicity of this type was first found in Cr2BeO4[11].
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Ji Group@Renmin University
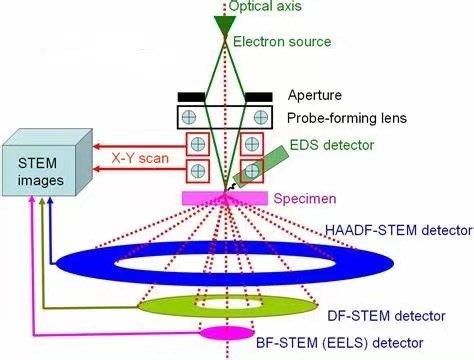
Manipulating and engineering atom dynamics with single atom precision has long been the ultimate goal in nanoscience and nanotechnology [1]. Direct atom manipulation or beam induced structural evolution by scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) has several advantages, i.e. much faster speed of atom manipulation (a few tens of seconds) and manipulation at room temperature [1]. STEM has been applied in various research, such as, structural defects [2], phase transitions [3], electron beam lithography [4], assembly of atoms [5] and single-atom migration [6].

Schematic of scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (STEM) System
When electrons pass through atomically thin 2D materials, energy can be either elastically or inelastically transferred to the targeted atom. During an elastic collision, impinging electrons are scattered to high angles by the recoiling nucleus and energy and momentum are both conserved. During the inelastic scattering process, the incident electron interacts with the electronic system of the target atom resulting in electronic excitation and electrostatic charging [1]
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Ji Group@Renmin University
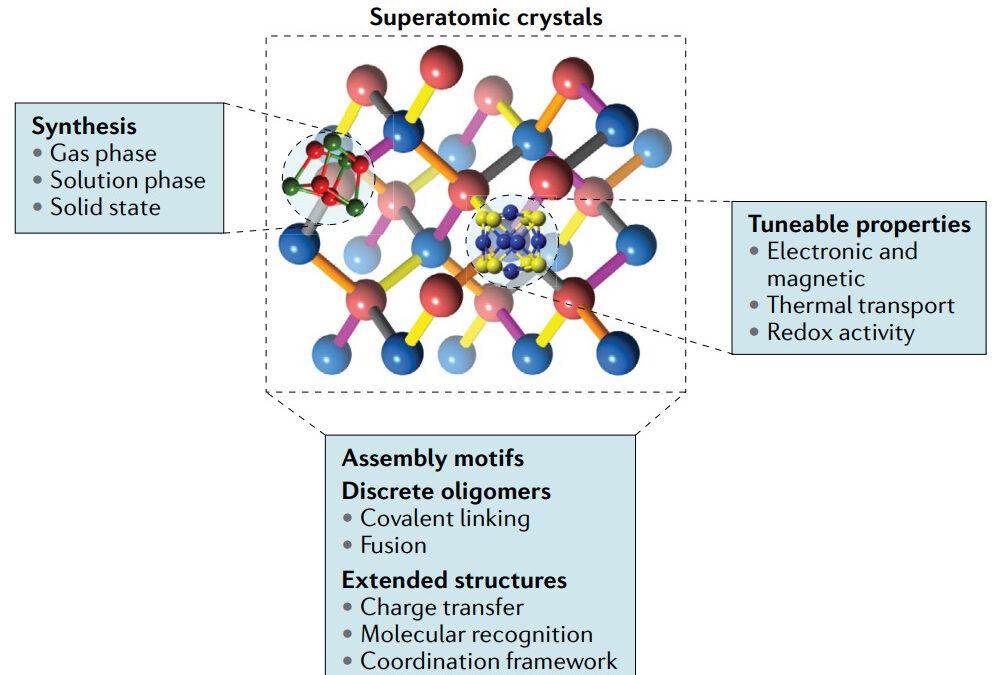

Superatomic crystals are typically prepared by combining structurally and electronically complementary superatoms in solution. Various tuneable molecular clusters can be used as superatomic building blocks, and by using different assembly motifs, these blocks can be assembled into materials. [Superatoms in materials science]
Atomic clusters, consisting of a few to a few thousand atoms, have emerged over the past 40 years as the ultimate nanoparticles. Some of these clusters form stable units with atomically precise structures that give rise to collective behaviors that mimic those of traditional atoms, essentially functioning as ‘superatoms’[1, 2]. The ultimate vision is to create materials with tailored and tuneable functions through the judicious design, synthesis and assembly of superatoms. The use of superatoms as building blocks for materials offers opportunities to design materials with tailored functionalities[3, 4].

Graphullerene, a two-dimensional crystalline polymer of C60, bridges the gulf between molecular and extended carbon materials. Its constituent fullerene subunits arrange hexagonally in a covalently interconnected molecular sheet.

Endohedral silicon cage V@Si12 clusters can construct two types of single cluster sheets exhibiting hexagonal porous or honeycomb-like framework with regularly and separately distributed V atoms. For the ground state of these two sheets, the preferred magnetic coupling is found to be ferromagnetic due to a free-electrons mediated mechanism. By using external strain, the magnetic moments and strength of magnetic coupling for these two sheets can be deliberately tuned, which would be propitious to their advanced applications.
However, the reinforcing chemical interaction between atoms (chemical bond)[5, 6]is the main factor that leads to the unstable structure of atomic crystal through the replacement of elements, and the weakening of such interaction is likely to overcome this difficulty. In the superatomic crystal materials with atomic clusters as the basic building unit, the surface saturated atomic clusters can be combined by non-covalent interactions such as weak atom identification, electrostatic interaction[7] and hydrogen bonding[8]. It has the potential to maintain structural stability in the regulation of electronic structural properties through continuous cluster (element) replacement, and is also more in line with the needs of large-scale material preparation, with some characteristics of atomic fabrication.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Ji Group@Renmin University
Correlated two-dimensional (2D) layers exhibit varies quantum phases, e.g. unconventional superconductor[1, 2], quantum spin liquids[3, 4], Mott and charge-transfer (CT) insulators[5-7], charge-density ware (CDW)[8, 9] and Wigner crystals[10-12], have been emerging in correlated systems. The understanding of correlated electronic systems and the phase transitions between those quantum states is very important.
The page you requested could not be found. Try refining your search, or use the navigation above to locate the post.
Ji Group@Renmin University